Drug Metabolism: How Your Body Processes Medications and Why It Matters
When you take a pill, it doesn’t just sit there waiting to help you. Your body is already at work breaking it down—this is drug metabolism, the process by which your body chemically transforms medications so they can be used or eliminated. Also known as medication processing, it’s the reason why two people taking the same dose can have totally different results. Some people feel the full effect right away. Others barely notice anything. That’s not luck—it’s your liver, your genes, and your kidneys doing their job differently.
At the heart of this is the liver enzymes, special proteins, mainly from the CYP450 family, that break down most drugs. These enzymes are like factory workers on an assembly line: some are fast, some are slow, and some get blocked by food, other meds, or even grapefruit juice. If your enzymes work too fast, the drug leaves your system before it can help. If they’re too slow, the drug builds up and causes side effects. That’s why drug interactions, when one medication changes how another is metabolized can be dangerous. A common painkiller might turn a heart drug into a toxic dose. Or a supplement you think is harmless could stop your antidepressant from working.
Your kidneys also play a big part. Once the liver breaks down a drug, the leftovers need to be flushed out. That’s where renal clearance, how efficiently your kidneys remove drug byproducts from your blood comes in. As you age or if you have kidney issues, this process slows down. That’s why older adults often need lower doses—not because they’re fragile, but because their bodies can’t clear the drugs like they used to. This is why lab monitoring calendars and dose adjustments for elderly patients aren’t just suggestions—they’re lifesavers.
And it’s not just about dosage. Some drugs trigger dangerous reactions because of how they’re metabolized. Think of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome or severe skin reactions—those aren’t random. They’re tied to specific genetic variations that affect how your body handles certain meds. Same with gout from bempedoic acid or tendon damage from antibiotics. These aren’t just side effects. They’re signals your metabolism is struggling.
Understanding drug metabolism isn’t about memorizing biochemistry. It’s about knowing why your meds work—or don’t—and why your doctor asks about every supplement, every beer, every new pill you take. It’s the invisible link between what you swallow and how you feel. Below, you’ll find real-world guides that show you exactly how this plays out with common drugs, what to watch for, and how to protect yourself from hidden risks.
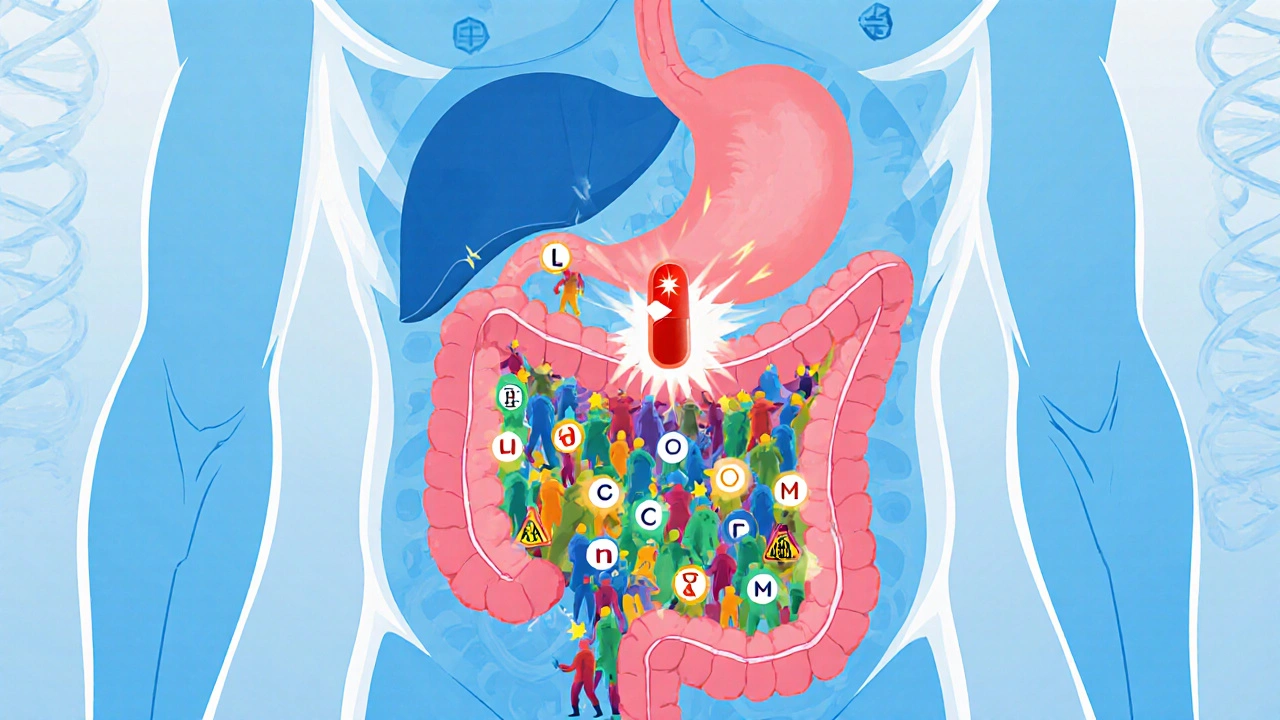
How Your Gut Bacteria Affect Drug Side Effects and Effectiveness
Your gut bacteria can turn medications into toxins or make them useless. Learn how microbiome-drug interactions cause unexpected side effects and what’s being done to personalize treatment.
view more