Chelation Therapy – What It Is and Why It Matters
When talking about Chelation Therapy, a medical process that uses chelating agents to bind and remove toxic metals from the body. Also known as metal chelation, it aims to lower metal load, improve organ function, and support overall health.
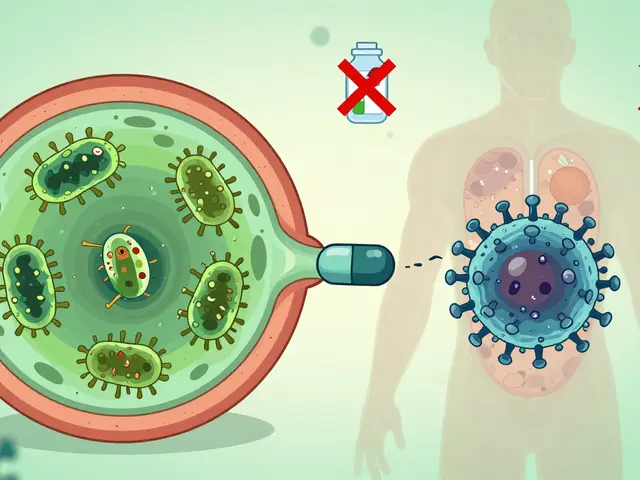
Chelation therapy is most often linked to Heavy Metal Poisoning, a condition where metals like lead, mercury, or arsenic accumulate and damage tissues. The therapy works by creating a chemical bond between the metal ions and the chelating agent, which the kidneys then flush out. This relationship—chelation therapy encompasses heavy metal detox—is the foundation of many clinical protocols.
How Chelation Therapy Works
The core of the process relies on Chelating Agents, substances like EDTA, DMSA, or DMPS that have a high affinity for metal ions. These agents act like a magnet, grabbing the metals and forming a stable complex that the body can safely eliminate. Because different agents target specific metals, doctors select the one that matches the patient's exposure profile. This selection step illustrates the semantic triple: chelating agents bind heavy metals, and chelation therapy uses chelating agents.
Beyond removing toxins, many users report that chelation therapy contributes to Detoxification, the broader process of clearing harmful substances and supporting metabolic balance. When metal load drops, oxidative stress often decreases, allowing antioxidant systems to work more efficiently. This cascade can influence cardiovascular health, skin appearance, and energy levels—a chain of effects that many clinicians monitor carefully.
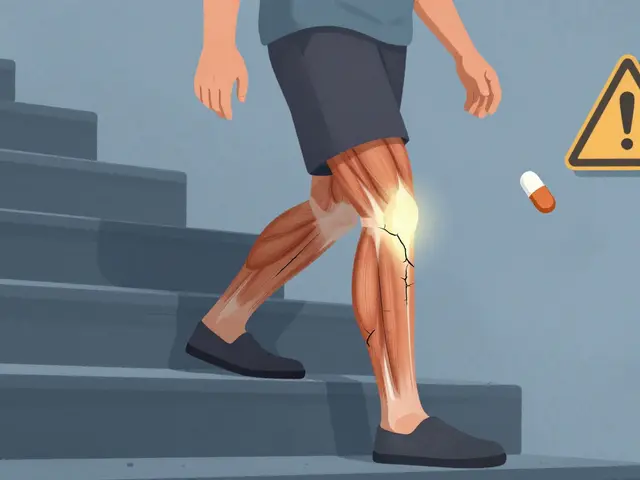
One area that sparks debate is the link between chelation therapy and Cardiovascular Health, the condition of the heart and blood vessels, especially regarding plaque reduction and improved blood flow. Some studies suggest that removing calcium and other metal deposits from arterial walls may slow atherosclerosis. The triple here is: chelation therapy reduces metal deposits, metal deposits contribute to plaque buildup, and plaque buildup impairs cardiovascular health. While evidence is mixed, many patients see measurable improvements in blood pressure and leg pain after a series of treatments.
Safety is a critical piece of the puzzle. Chelation therapy requires medical supervision to avoid side effects like electrolyte imbalances or kidney strain. A qualified practitioner will assess baseline metal levels, kidney function, and heart health before starting a protocol. This ensures the therapy targets the right problem without creating new ones. In the sections below you’ll find practical guides, safety checklists, and real‑world experiences that show how to navigate the process responsibly.
Now that you understand the basics—what chelation therapy is, how chelating agents work, and why it matters for detox and heart health—take a look at the curated articles below. They dive deeper into dosing schedules, patient stories, and the latest research, giving you the tools to decide if this approach fits your health goals.
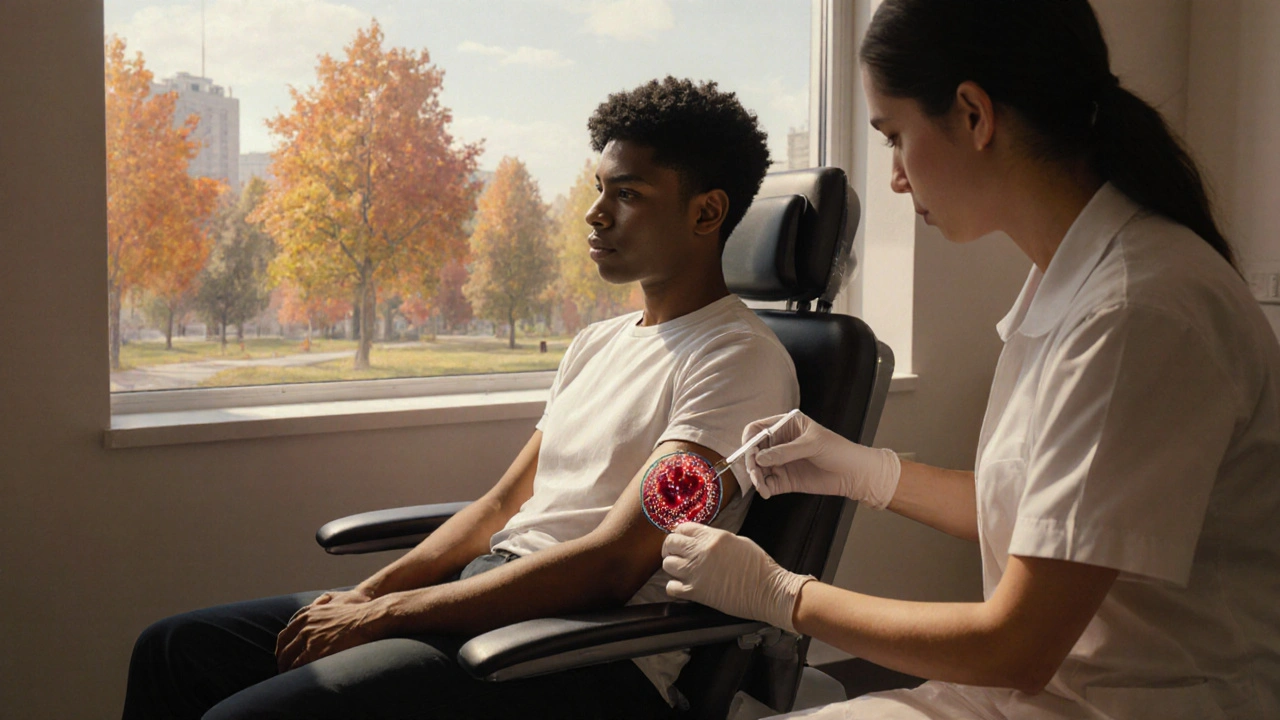
Bone Marrow Disorders and Iron Overload: How They're Linked
Explore how bone marrow disorders like thalassemia, sickle cell disease, and MDS lead to iron overload, its health risks, diagnosis, and management strategies.
view more