SGLT2 Inhibitors: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When you hear SGLT2 inhibitors, a class of oral diabetes medications that lower blood sugar by making the kidneys remove glucose through urine. Also known as gliflozins, they’re not just another pill—they’re changing how we treat type 2 diabetes and even protect the heart and kidneys. Unlike older drugs that force your body to make more insulin or make cells more sensitive to it, SGLT2 inhibitors let your body do the work naturally. They block a protein in your kidneys called SGLT2, which normally reabsorbs sugar back into your blood. When it’s blocked, that extra sugar just leaves through your pee. Simple. No magic. Just biology.
That’s why these drugs don’t cause low blood sugar on their own—you can’t remove more sugar than your body has. And because they pull out grams of glucose daily, many people lose a few pounds without trying. But the real surprise? They don’t just help with blood sugar. Studies show people taking SGLT2 inhibitors like empagliflozin, a specific SGLT2 inhibitor proven to reduce heart failure hospitalizations and kidney decline in diabetic patients or dapagliflozin, another SGLT2 inhibitor with strong evidence for heart and kidney protection have fewer heart attacks, less heart failure, and slower kidney damage. That’s rare. Most diabetes drugs only manage glucose. These actually change outcomes.
But they’re not without trade-offs. Because you’re peeing out sugar, you might get more yeast infections or urinary tract infections. Dehydration is a risk, especially if you’re on diuretics or in hot weather. And in rare cases, a serious infection called ketoacidosis can happen—even when blood sugar isn’t sky-high. That’s why monitoring matters. You don’t need to avoid these drugs, but you do need to know what to watch for. The posts below cover exactly that: real side effects, how they compare to other diabetes treatments, what labs to track, and how to stay safe while using them.
Whether you’re on one of these drugs already, considering it, or just trying to understand why your doctor mentioned it, this collection gives you the straight talk you won’t get from a pamphlet. From how they stack up against GLP-1s like Rybelsus to what to do if you get a UTI, you’ll find practical, no-fluff answers here.
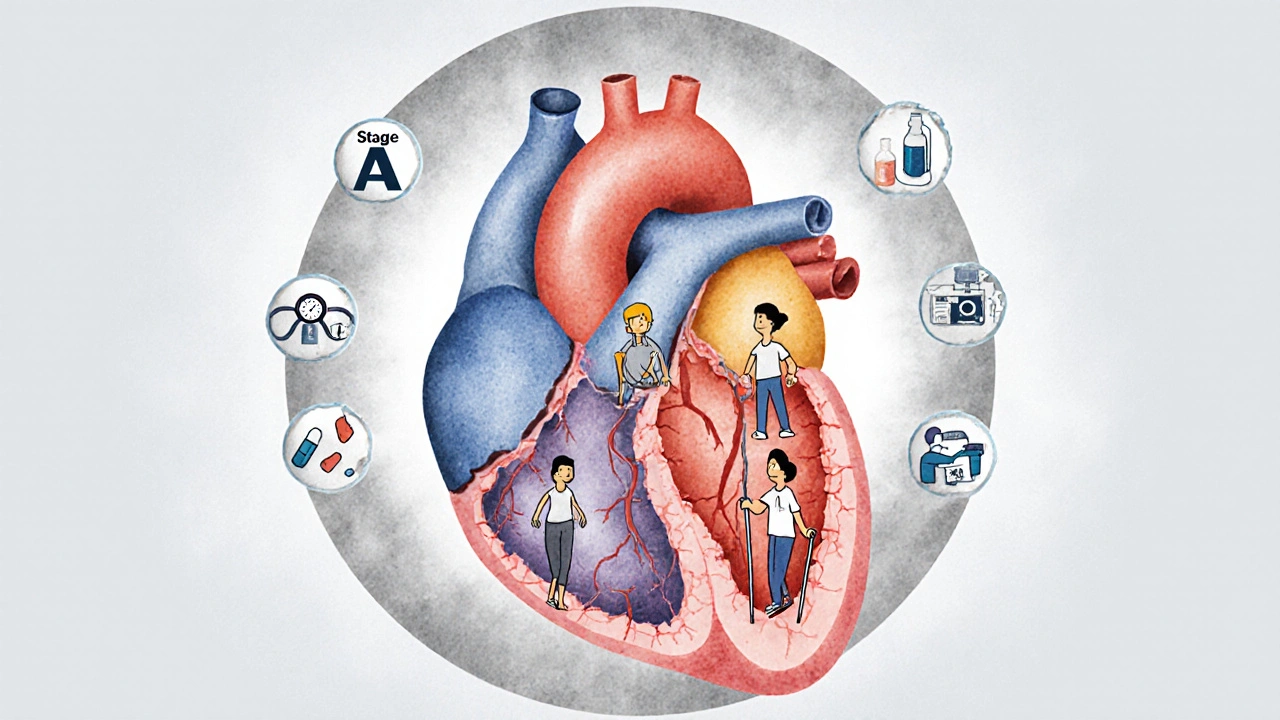
Heart Failure Management: From Diagnosis to Living Well
Heart failure management has changed dramatically. With new drugs like SGLT2 inhibitors and advanced monitoring tools, patients are living longer and better than ever. Learn how diagnosis, treatment, and daily care have evolved.
view more