Antihistamine Side Effects: What You Need to Know Before Taking Them
When you take an antihistamine, a medication used to block histamine, a chemical your body releases during allergic reactions. Also known as allergy pills, they help with sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes—but they don’t all act the same. Some make you so sleepy you can’t drive. Others barely touch your energy. The difference comes down to whether it’s a first-generation or second-generation antihistamine.
First-generation antihistamines, like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and chlorpheniramine, are old-school. They cross into your brain easily, which is why they cause drowsiness, dry mouth, and sometimes confusion in older adults. These aren’t just side effects—they’re expected. People used to take them as sleep aids because of it. But if you’re working, driving, or caring for kids, this isn’t just inconvenient—it’s risky. On the flip side, second-generation antihistamines, including cetirizine (Zyrtec), loratadine (Claritin), and fexofenadine (Allegra), were designed to stay out of the brain. They work just as well for allergies but rarely cause drowsiness in most people. Still, a few individuals report tiredness even with these—especially at higher doses or when mixed with alcohol or other meds. That’s why knowing your body matters more than the brand name.
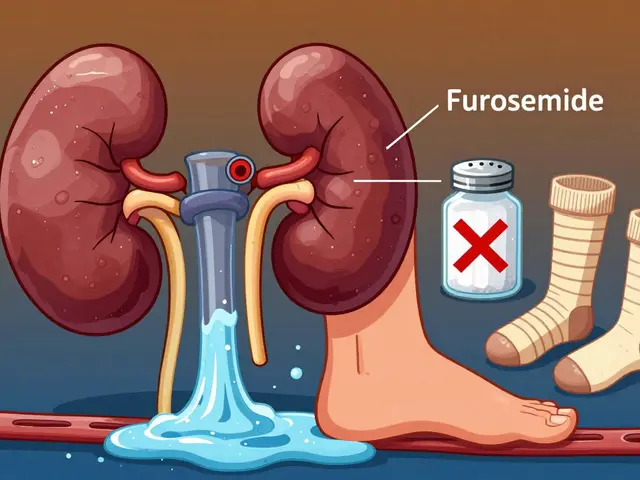
It’s not just about sleepiness. Antihistamines can mess with your bladder, making it harder to urinate—especially if you’re male and have an enlarged prostate. They can raise your heart rate, dry out your eyes, and in rare cases, trigger confusion or hallucinations in older adults. If you’re over 65, taking multiple meds, or have liver or kidney issues, you’re more vulnerable. Even over-the-counter pills can be dangerous if used long-term without checking in with a doctor.
And don’t forget drug interactions. Mixing antihistamines with sleep aids, painkillers, or even some antidepressants can turn a mild side effect into a serious one. You might not realize you’re doubling up until you feel too drowsy to stand. That’s why keeping a list of everything you take—even herbal supplements—is one of the smartest things you can do.
What you’ll find below are real, practical breakdowns of how these drugs work, who’s most at risk, and which ones actually deliver relief without the fog. No fluff. No marketing. Just what you need to know before the next pill goes in your mouth.
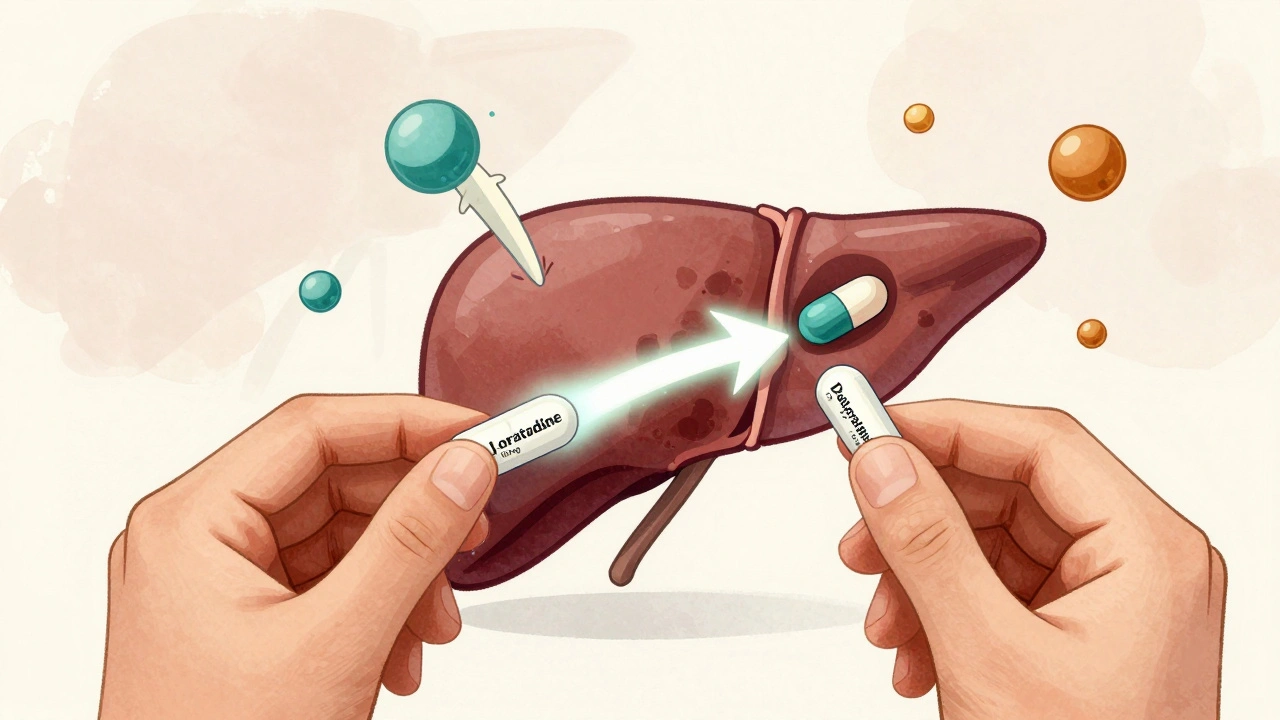
Desloratadine vs Loratadine: Which Antihistamine Is Better for Allergy Relief?
Desloratadine and loratadine are both non-sedating antihistamines for allergies, but desloratadine is stronger, longer-lasting, and better for congestion and kids under 2. Learn which one works best for your symptoms.
view more