Neuroscience: Practical guides on the nervous system
Your nervous system controls movement, sensation, digestion and mood. On this Neuroscience page you'll find clear, practical posts about how medicines affect nerves, what side effects to watch for, and how to choose reliable pharmacies. Want straightforward explanations without jargon? You're in the right place.
How drugs like butylscopolamine work
One recent post covers butylscopolamine, an antispasmodic used for stomach and intestinal cramps. It blocks acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors on smooth muscle, which calms unwanted contractions. Because butylscopolamine is a quaternary ammonium compound, it stays mostly outside the brain — that means it acts on the gut without strong central nervous system effects. Common results are less cramping and faster relief for spasms.
Side effects you might notice include dry mouth, blurred vision, a faster heartbeat, or trouble urinating. Those come from the same anticholinergic action but in other parts of the body. If you have glaucoma, urinary retention, or certain heart issues, tell your prescriber — the drug can make those problems worse. Pregnant or breastfeeding? Ask a clinician before using it.
Choosing safe online pharmacies and getting meds right
Buying meds online can save time, but safety matters. Check that the pharmacy requires a prescription, displays licensing information, and has clear contact details. Look for secure checkout (https), readable shipping and refund policies, and honest reviews. If a price looks unbelievably low, that’s a red flag — quality and proper storage matter for medications.
When you order a nervous-system drug, confirm the exact active ingredient, dose, and form (tablet vs. injection). If instructions differ from what your doctor told you, contact them or the pharmacy’s pharmacist before taking the medicine. Keep a list of your current meds handy to avoid interactions — anticholinergic drugs like butylscopolamine can interact with others and increase side effects.
What to watch for after taking an antispasmodic: significant dizziness, very fast heartbeat, severe blurred vision, signs of an allergic reaction (rash, swelling, trouble breathing), or inability to urinate. Any of those should prompt immediate medical attention. For mild effects like dry mouth, simple measures — sipping water, chewing sugar-free gum — help a lot.
If you want more depth, read the full post on butylscopolamine for a clear breakdown of how it works and when doctors prescribe it. Browse other Neuroscience posts here for short, practical articles on nerve-related drugs, basic conditions, and how to stay safe when buying medications online. Have a question about a symptom or a drug? Ask your healthcare provider — and then come back here for plain-language answers and reliable pharmacy tips.
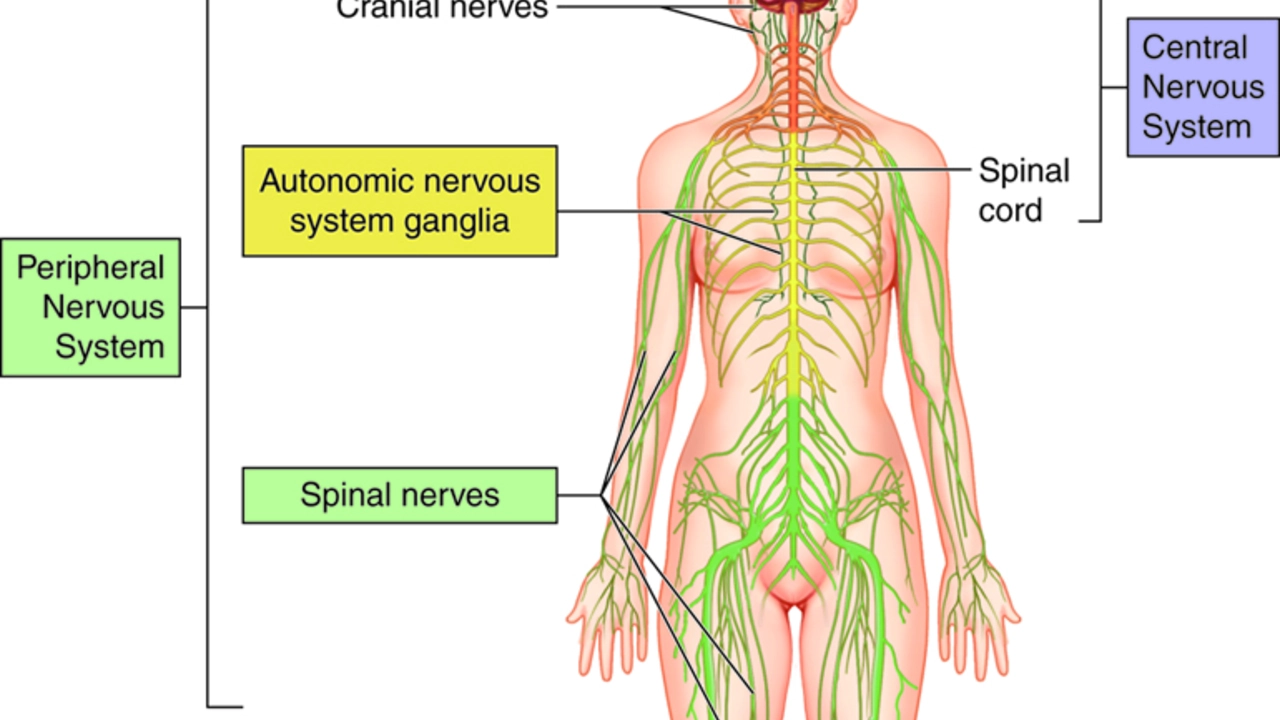
Butylscopolamine and its impact on the nervous system
As a blogger, I recently came across the topic of Butylscopolamine and its impact on the nervous system. It turns out that Butylscopolamine is an antispasmodic drug that helps to ease muscle cramps and spasms in the stomach and intestines. It works by blocking the action of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which is responsible for muscle contractions. By doing so, it helps to alleviate pain and discomfort caused by these spasms. I found it fascinating to learn about this drug and its role in managing various gastrointestinal issues.
view more