Understanding Butylscopolamine
Before diving into the impact of butylscopolamine on the nervous system, it is essential to understand what this compound is and its primary uses. Butylscopolamine, also known as hyoscine butylbromide or scopolamine butylbromide, is an anticholinergic drug that is primarily used to treat abdominal pain and spasms. It is also effective in alleviating symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and relieving menstrual cramps.
The drug works by blocking the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells and muscles. By doing so, it helps relax the smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract, thus reducing pain and discomfort. Now that we have a basic understanding of butylscopolamine, let's explore its impact on the nervous system.
Butylscopolamine and the Central Nervous System
While butylscopolamine primarily targets the peripheral nervous system (PNS), it also has some effects on the central nervous system (CNS). The blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from harmful substances, generally prevents butylscopolamine from entering the CNS. However, in some cases, the drug may cross this barrier and cause side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and confusion.
It is important to note that these side effects are relatively rare, and the risk of experiencing them increases with higher doses of the drug. Therefore, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage to minimize the risk of these side effects.
Butylscopolamine's Impact on Acetylcholine
As mentioned earlier, butylscopolamine works by blocking the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for transmitting signals between nerve cells and muscles. Acetylcholine is a crucial neurotransmitter in both the PNS and the CNS, and it plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including muscle movement, memory, and learning.
By blocking the action of acetylcholine, butylscopolamine can help alleviate muscle spasms and pain in the gastrointestinal tract. However, this action can also lead to some side effects, particularly when the drug affects the CNS. These side effects may include dry mouth, blurred vision, and urinary retention.
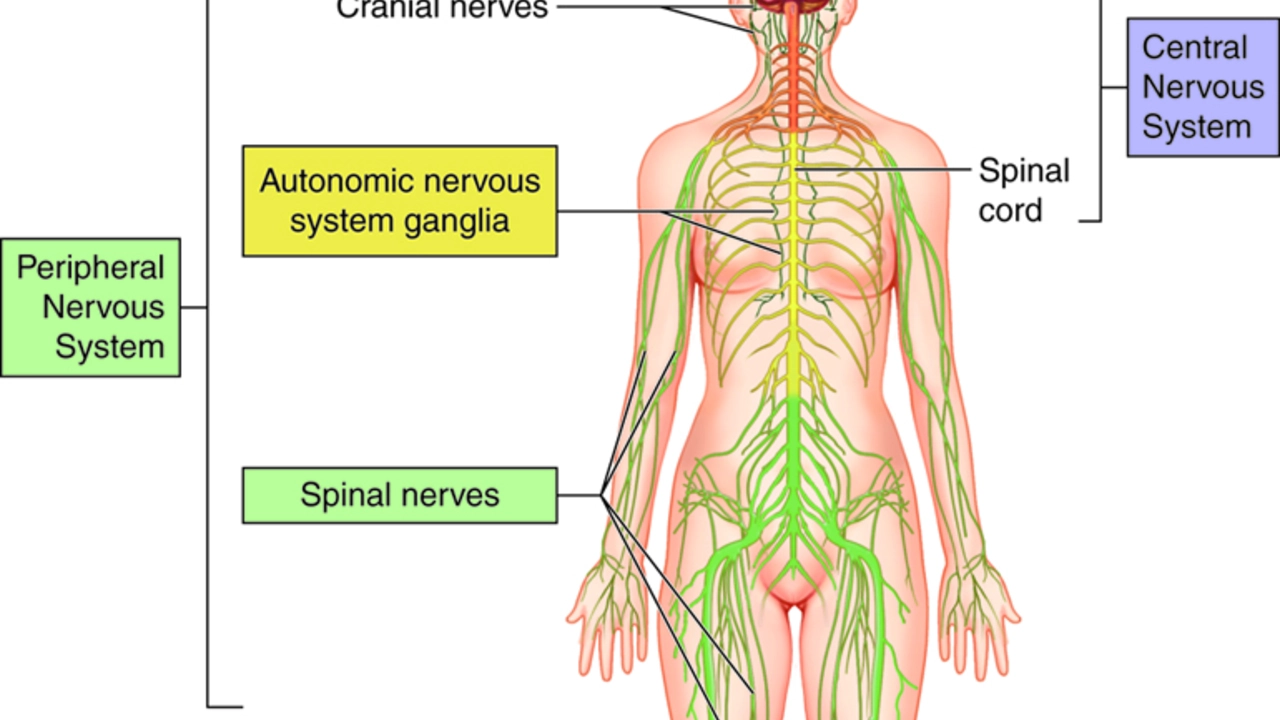
Butylscopolamine and the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a part of the PNS responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as digestion, heart rate, and blood pressure. The ANS is further divided into two branches: the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS). Acetylcholine is an essential neurotransmitter in the PNS, and its inhibition by butylscopolamine can impact the ANS.
By blocking the action of acetylcholine, butylscopolamine can lead to a decrease in the activity of the PNS, which may result in side effects such as increased heart rate, dry mouth, and constipation. These side effects are generally mild and can be managed by following the prescribed dosage and discussing any concerns with your healthcare provider.
Butylscopolamine's Role in Treating Motion Sickness
Although butylscopolamine is primarily used to treat abdominal pain and spasms, it is also sometimes prescribed to help prevent motion sickness. Motion sickness occurs when the brain receives conflicting signals from the inner ears, eyes, and muscles, leading to symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, and vomiting. Acetylcholine plays a role in transmitting these conflicting signals, and by blocking its action, butylscopolamine can help alleviate motion sickness symptoms.
It is essential to note that butylscopolamine is not the first-line treatment for motion sickness, and other medications, such as dimenhydrinate or meclizine, are typically prescribed first. However, butylscopolamine may be a suitable option for those who do not respond well to these medications or experience significant side effects from them.
Butylscopolamine's Effect on the Circulatory System
While the primary focus of butylscopolamine is on the nervous system, it also has some effects on the circulatory system. By blocking the action of acetylcholine, butylscopolamine can cause blood vessels to constrict, leading to an increase in blood pressure. This effect is generally mild and does not pose a significant risk for most individuals.
However, individuals with a history of high blood pressure or other cardiovascular conditions should discuss the potential risks and benefits of taking butylscopolamine with their healthcare provider before starting the medication.
Potential Drug Interactions
Butylscopolamine can potentially interact with other medications, which may affect its efficacy or increase the risk of side effects. Some common medications that may interact with butylscopolamine include antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, and other anticholinergic drugs.
If you are taking any of these medications or are concerned about potential drug interactions, it is essential to discuss your concerns with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the best course of action to ensure that you receive the most effective treatment with the least risk of side effects.
Precautions and Contraindications
While butylscopolamine is generally safe for most individuals, there are some precautions and contraindications to be aware of. Individuals with a history of glaucoma, urinary retention, or bowel obstructions should avoid taking butylscopolamine, as it may exacerbate these conditions.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before taking butylscopolamine, as its safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been well-established. Additionally, individuals with a history of seizures, heart conditions, or kidney or liver disease should discuss the potential risks and benefits of taking butylscopolamine with their healthcare provider.
Conclusion
In summary, butylscopolamine is an effective medication for treating abdominal pain and spasms, as well as other conditions like motion sickness. Its impact on the nervous system primarily involves blocking the action of acetylcholine, which can lead to various side effects, particularly when the drug affects the CNS. By understanding these effects and following the prescribed dosage, most individuals can safely take butylscopolamine and experience its benefits without significant side effects.




17 Comments
Just a heads‑up, the drug’s anticholinergic action can make you feel a bit dry‑mouthy, but most folks handle it fine.
This stuff works only if you follow the dose
Ah, the noble quest to block acetylcholine-because who doesn't love a little brain fog with their stomach relief?
Hey everyone, just a friendly reminder that if you have hypertension, you might want to chat with your doc before adding this to your regimen; it's all about balance.
Indeed, the pharmacodynamics of butylscopolamine, while primarily peripheral, may-under certain circumstances-cross the blood‑brain barrier, leading to drowsiness, dizziness, or, albeit rarely, confusion.
If you notice dry mouth, stay hydrated and consider sugar‑free gum.
The notion that butylscopolamine simply confines itself to the gastrointestinal tract is, frankly, a charmingly naive misconception.
While the drug’s quaternary ammonium structure does impede its penetration of the blood‑brain barrier, it does not render it completely impermeable.
Clinicians have reported occasional central effects, especially in patients with compromised barrier integrity.
One must also consider the pharmacokinetic variability introduced by hepatic metabolism, which can subtly alter plasma concentrations.
Higher dosages, as the literature suggests, increase the probability of central side effects such as dizziness and, in rare cases, delirium.
Conversely, the peripheral anticholinergic action remains the cornerstone of its therapeutic efficacy against smooth‑muscle spasms.
By antagonizing muscarinic receptors, the drug reduces involuntary contractions, thereby alleviating abdominal pain.
However, this same antagonism also diminishes salivary secretions, leading to the well‑known xerostomia that many patients find bothersome.
Moreover, the blockade of muscarinic receptors within the eyes can precipitate blurred vision, which some patients mistake for a neurological deficit.
In the autonomic realm, the sympathetic‑parasympathetic balance can shift, occasionally resulting in tachycardia.
Patients with pre‑existing cardiovascular conditions should be monitored closely, as even mild tachycardia may pose a risk.
The drug’s impact on the central nervous system, though minimal, can be amplified when combined with other anticholinergic agents.
Polypharmacy, especially in the elderly, is a notorious catalyst for cumulative anticholinergic burden.
Thus, a thorough medication reconciliation is not just advisable but essential before initiating butylscopolamine therapy.
In summary, while butylscopolamine is a valuable tool in the clinician’s arsenal, its use demands a nuanced appreciation of both peripheral benefits and potential central drawbacks.
Let’s give a shout‑out to the folks who get relief without the brain fog-nice work, meds! 😊👍
People woudnt realliy kno about thoses side efects untill they experince them-so be cautios.
Sometimes I feel like the world forgets how many side‑effects those pills carry.
It's absolutely unacceptable to ignore contraindications; people with glaucoma must never be handed this drug.
Butylscopolamine blocks ACh raises BP.
Hey folks, think of the drug as a gentle tide that smooths out the choppy seas of gut cramps-pretty neat!
You know, the pharma giants love to downplay the CNS penetration of butylscopolamine; it's part of the grand design to keep us dependent on their pricey combos 😊.
Stay positive-most people tolerate the medication well and can enjoy relief without trouble.
Wow, what a cascade of effects-dry mouth, blurred vision, a racing heart, and yet, here we are, hoping for a little comfort, all while the drug dances delicately between peripheral relief and the faint whisper of central intrusion, reminding us that every pill carries its own symphony of consequences, and we, the humble listeners, must decide which notes we’re willing to endure.
While I relish a good drama, let’s keep it real: the drug does its job, but watch for those pesky side effects.