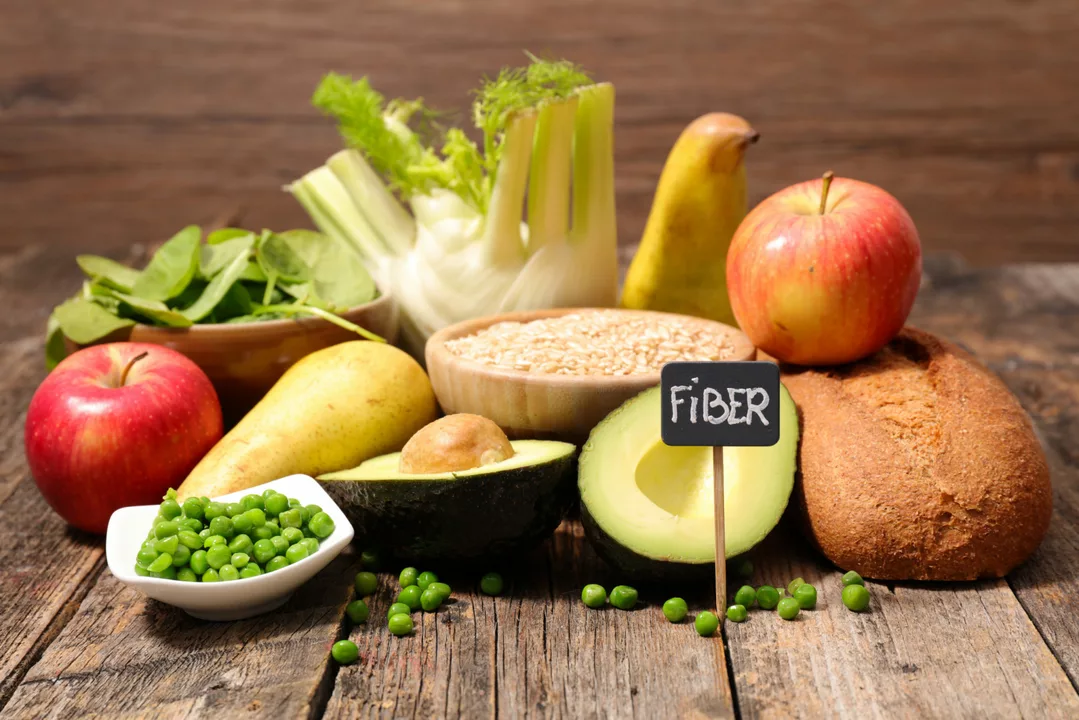

Understanding Chronic Diarrhea and the Importance of Fiber
As someone who has dealt with chronic diarrhea, I know first-hand how frustrating and debilitating it can be. It not only affects your quality of life, but also your confidence and emotional well-being. One of the key factors in managing chronic diarrhea is understanding the role of fiber in your diet. In this article, I will discuss the importance of fiber, what to eat and what to avoid to help manage chronic diarrhea.
Types of Fiber: Soluble and Insoluble Fiber
Before we dive into the best foods for managing chronic diarrhea, it's essential to understand the two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that slows down digestion. This type of fiber helps to regulate bowel movements and can be beneficial in managing diarrhea. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, helping to prevent constipation. However, it's important to note that too much insoluble fiber can actually worsen diarrhea.
Foods Rich in Soluble Fiber: What to Eat
Eating foods rich in soluble fiber can help improve the consistency and frequency of bowel movements, providing relief from chronic diarrhea. Some of the best sources of soluble fiber include:
1. Oatmeal
Oatmeal is an excellent source of soluble fiber, making it a great breakfast option for those dealing with chronic diarrhea. It can help to slow down digestion, allowing more water to be absorbed by the stool and reducing the frequency of diarrhea episodes.
2. Fruits
Many fruits contain soluble fiber, with some of the best options being apples, bananas, and berries. These fruits can help to regulate bowel movements and provide relief from diarrhea. However, it's important to avoid fruits with high amounts of fructose, as this can worsen diarrhea in some individuals.
3. Legumes
Beans, lentils, and peas are all good sources of soluble fiber and can be included in the diet to help manage chronic diarrhea. However, it's important to introduce these foods gradually, as they can cause gas and bloating in some individuals.
Foods High in Insoluble Fiber: What to Avoid
While insoluble fiber is essential for overall digestive health, it may not be the best option for those dealing with chronic diarrhea. Some common sources of insoluble fiber that you may want to limit or avoid include:
1. Whole Grains
Whole grains such as whole wheat, brown rice, and quinoa are high in insoluble fiber, which can exacerbate diarrhea. Instead, opt for refined grains like white rice or white bread, which are lower in fiber and may be easier to digest.
2. Nuts and Seeds
While nuts and seeds are a healthy snack option, they are also high in insoluble fiber and can worsen diarrhea. If you're dealing with chronic diarrhea, it's best to limit your intake of these foods or choose options that are lower in fiber, such as nut butters.
3. Raw Vegetables
Raw vegetables, especially those with tough skins and seeds, can be difficult to digest and may worsen diarrhea. Instead, opt for cooked vegetables or choose options that are lower in insoluble fiber, such as zucchini or squash.
Hydration and Electrolytes: Key Components in Managing Chronic Diarrhea
Dehydration is a common concern for those dealing with chronic diarrhea, as the body loses vital fluids and electrolytes. It's essential to drink plenty of water and consume electrolyte-rich foods, such as coconut water or sports drinks, to help maintain proper hydration levels. Additionally, avoiding caffeine and alcohol can help prevent further dehydration.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional: Tailoring Your Diet to Your Needs
While incorporating soluble fiber and avoiding insoluble fiber can be beneficial in managing chronic diarrhea, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a nutritionist or gastroenterologist, to create a personalized diet plan. They can help identify any food intolerances or allergies that may be contributing to your symptoms and provide recommendations on the best foods to include or avoid in your diet.
Conclusion: Finding Relief from Chronic Diarrhea
Managing chronic diarrhea can be challenging, but understanding the role of fiber in your diet and making appropriate dietary changes can help provide relief. By focusing on soluble fiber-rich foods, avoiding insoluble fiber, and maintaining proper hydration, you can take control of your symptoms and improve your overall digestive health. Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet.



9 Comments
Solid advice, thanks! 😊
Yo, I think you’re kinda missing the mark on whole grains – you don’t have to ditch *every* grain, just the ones that are super rough on the gut. In fact, white rice can be a lifesaver when you’re battling the runs, and it’s totally fine to swap it in for brown rice sometimes. Also, keep an eye on the fructose content in fruits, cuz that stuff can really stir up a storm in your stomach if you’re sensitive. And yeah, don’t forget a splash of probiotic yogurt; it might just be the sidekick you never knew you needed.
I hear you and I get how tough it can be. It’s good to focus on soluble fiber and stay hydrated. Your body will thank you over time. Keep listening to what it tells you.
Alright, squad, let’s power up with oatmeal each morning – it’s like a fiber fortress that slows digestion and gives your stool some much‑needed bulk. Toss in a banana or some berries for that sweet soluble boost without the fructose overload. And if you’re feeling adventurous, slide a spoonful of plain kefir into your routine for extra probiotic love. Remember, staying consistent is the secret sauce, so keep at it and watch the symptoms mellow.
Listen up, you’ve got to cut the nuts and seeds right now – they’re flooding your system with insoluble fiber and that’s a recipe for disaster when you’re dealing with chronic diarrhea. Swap them for smooth nut butter or better yet, go plain with boiled potatoes and white rice until things settle. Hydration isn’t optional, so chug water and grab an electrolyte drink every few hours. Stop messing around and follow the plan, or you’ll stay stuck in the same miserable loop.
I concur with the preceding counsel and would add that a measured introduction of legumes, beginning with a modest half‑cup portion, can facilitate adaptation of the gut microbiota without precipitating excessive gas. Moreover, adherence to a structured hydration schedule-preferably involving isotonic solutions-will mitigate electrolyte loss inherent to frequent bowel movements. Should symptoms persist, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is advisable to tailor the regimen further.
Great tips! Keep it up.
Honestly, the entire premise of glorifying "soluble fiber" as a panacea for chronic diarrhea is nothing short of nutritional folklore masquerading as science. You’re led to believe that a spoonful of oatmeal will magically seal the leaky gut, when in reality the gut is a complex ecosystem that resists such simplistic fixes. The article conveniently glosses over the fact that individual tolerances can swing wildly from one person to the next, yet it offers a one‑size‑fits‑all menu that would make a fast‑food franchise jealous. Moreover, the suggestion to ditch whole grains altogether is a reckless endorsement of refined carbohydrates, which, let’s be real, are the very culprits of modern metabolic decay. By championing white rice and refined bread, the piece implicitly encourages a dietary regression that could sabotage long‑term gut health. If you scrutinize the language, you’ll notice an unsettling lack of nuance, as if the author were drafting a marketing brochure for a bland diet plan. The call to "avoid raw vegetables" ignores the fact that many patients thrive on lightly steamed greens, which provide essential micronutrients without the fibrous trauma. And do not forget the glaring omission of prebiotic foods that nourish beneficial bacteria, a glaring blind spot for anyone serious about gut flora. The hydration advice, while valid, is presented with the enthusiasm of a tech salesman hawking an electrolyte drink, rather than the sober caution a medical professional would employ. Let’s not overlook the passive voice that permeates the text, shielding the author from accountability for the sweeping generalizations. In short, the article is a patchwork of half‑truthed statements stitched together with good intentions but lacking rigorous scientific grounding. Readers deserve more than a checklist of "do this, avoid that"; they deserve a critical appraisal of the evidence, which is conspicuously absent. So, before you blindly adopt the recommended regimen, demand peer‑reviewed sources and perhaps a second opinion from a qualified gastroenterologist. Otherwise, you risk trading one set of symptoms for another, all under the illusion of having found the ultimate cure. Take control of your health with informed choices, not with marketing copy.
I think you missed the main point about personal tolerance, and that’s why many still suffer.