ACE Inhibitors: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your heart or blood vessels are under stress, ACE inhibitors, a class of medications that block the angiotensin-converting enzyme to lower blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart. Also known as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, they help relax blood vessels and decrease fluid buildup—making them one of the most prescribed treatments for high blood pressure and heart failure. Unlike some drugs that just mask symptoms, ACE inhibitors target the body’s own stress response system. That’s why doctors reach for them not just for hypertension, but also after heart attacks, in kidney disease, and for people with diabetes who need extra protection for their kidneys.
They work by stopping the body from turning angiotensin I into angiotensin II, a powerful chemical that narrows blood vessels and raises blood pressure. Less angiotensin II means your arteries open up, your heart doesn’t have to work as hard, and your kidneys flush out extra salt and water. This simple mechanism is why drugs like lisinopril, enalapril, and ramipril show up in so many treatment plans. But they’re not for everyone. Some people get a dry cough, others face rare but serious side effects like angioedema. And if your kidneys are already weak, your doctor will monitor you closely—because these drugs can affect kidney function, especially in older adults.
What’s interesting is how ACE inhibitors connect to other treatments you might see in the posts below. For example, heart failure, a condition where the heart can’t pump blood effectively. Also known as congestive heart failure, it’s one of the main reasons ACE inhibitors are used long-term. Many of the posts here talk about newer drugs like SGLT2 inhibitors that now work alongside ACE inhibitors to improve survival rates. Then there’s blood pressure medication, a broad category that includes beta-blockers, diuretics, and calcium channel blockers. Also known as antihypertensives, it’s worth noting that ACE inhibitors are often the first line—not because they’re the cheapest, but because they’ve been proven to reduce strokes and heart attacks over time. You’ll also see posts about kidney function, elderly dosing, and drug interactions—all directly tied to how ACE inhibitors behave in the body.
If you’re on one of these drugs, you’re not alone. Millions take them daily. But knowing why you’re taking it, what to watch for, and how it fits with other meds can make a real difference. The posts below dive into real cases: how kidney health affects dosing, what happens when you mix them with NSAIDs, why some people switch to ARBs instead, and how monitoring your labs can prevent hidden problems. This isn’t just theory—it’s what people are actually dealing with in clinics and pharmacies every day.
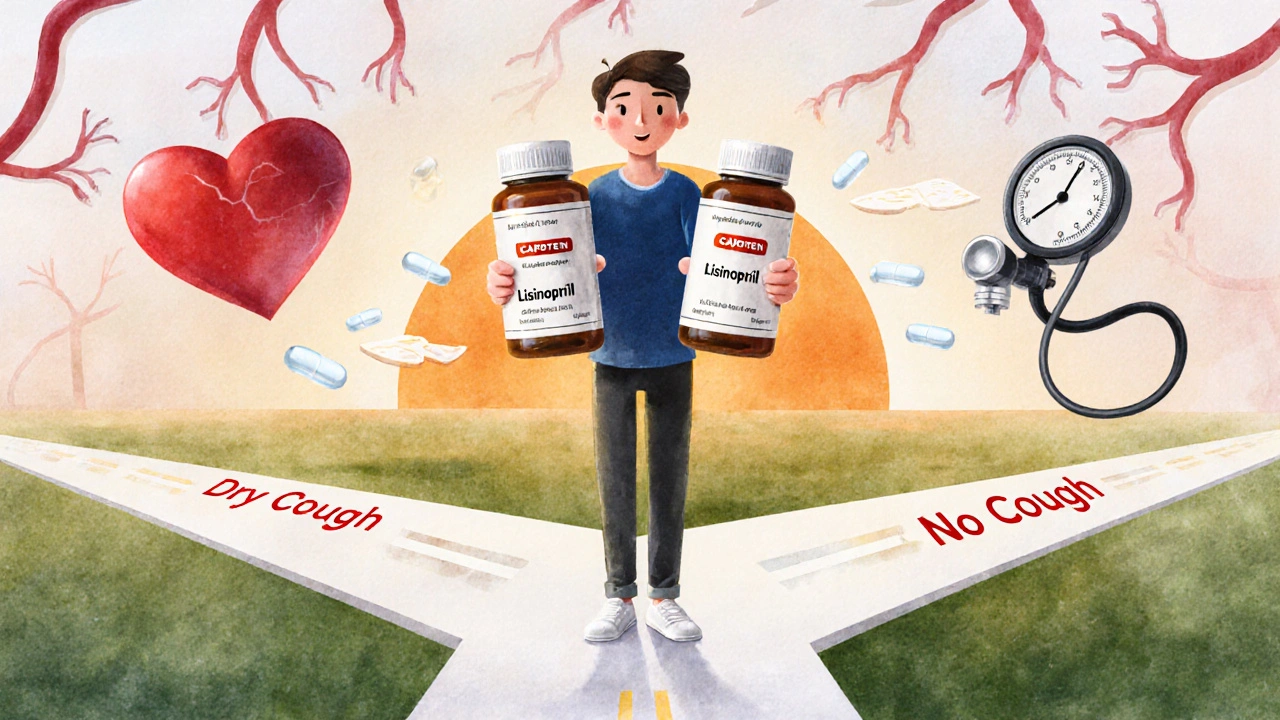

Capoten (Captopril) vs Alternatives: What Works Best for High Blood Pressure?
Capoten (captopril) is an older blood pressure medication with common side effects like dry cough. Learn how lisinopril, losartan, amlodipine, and other alternatives compare in effectiveness, cost, and tolerability.
view more