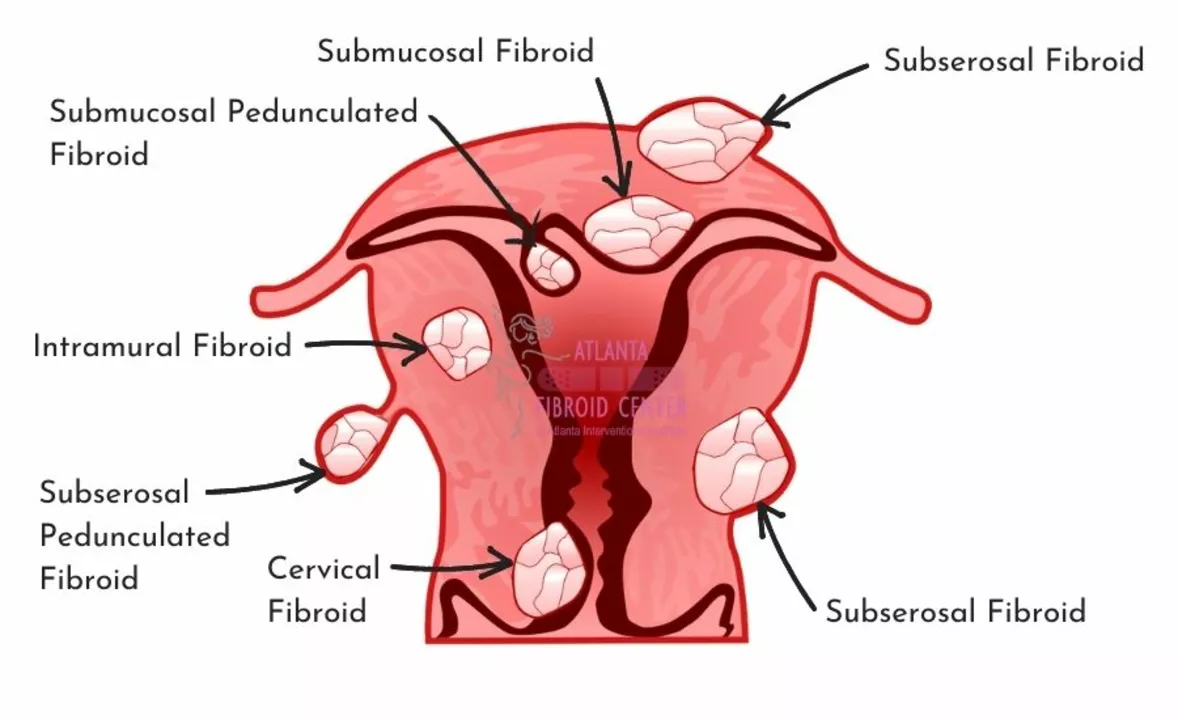
Understanding the Uterus and Its Lining
The uterus plays a crucial role in the female reproductive system, and maintaining its health is essential for overall well-being. The lining of the uterus, also known as the endometrium, is a layer of tissue that thickens during the menstrual cycle to prepare for the potential implantation of a fertilized egg. If a pregnancy does not occur, the lining sheds during menstruation. However, sometimes the endometrium grows too thick, a condition known as endometrial hyperplasia, which can lead to abnormal bleeding. In this article, we will delve into the causes and symptoms of this condition and discuss available treatments.
Endometrial Hyperplasia: The Overgrowth of the Uterine Lining
Endometrial hyperplasia occurs when the cells in the lining of the uterus multiply at an abnormal rate, causing the endometrium to thicken beyond its normal range. This overgrowth can be triggered by several factors, including hormonal imbalances, obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and use of certain medications. When the endometrium becomes too thick, it can lead to complications such as abnormal bleeding, which can manifest as heavy or prolonged periods, bleeding between periods, or even postmenopausal bleeding.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Since abnormal uterine bleeding can be a sign of endometrial hyperplasia or other health concerns, it's essential to recognize the symptoms and seek medical attention if necessary. Some common signs of abnormal bleeding include:
- Periods that last longer than seven days
- Bleeding that soaks through one or more pads or tampons every hour for several hours in a row
- Bleeding between periods
- Spotting or bleeding after intercourse
- Heavier than usual menstrual flow
- Menstrual cycles shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing Endometrial Hyperplasia and Abnormal Bleeding
To diagnose the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding, your healthcare provider will likely perform a physical examination, review your medical history, and order laboratory tests. They may also perform a pelvic ultrasound to evaluate the thickness of your endometrium and determine if there are any abnormalities in the uterus. In some cases, an endometrial biopsy may be necessary to collect a small sample of the uterine lining for further testing. This can help confirm the presence of endometrial hyperplasia and rule out other potential causes of abnormal bleeding, such as endometrial cancer.
Treatment Options for Endometrial Hyperplasia and Abnormal Bleeding
Once a diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia has been made, your healthcare provider will discuss appropriate treatment options. These may include:
- Hormonal therapy, such as progestin, to help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce endometrial growth
- Intrauterine device (IUD) that releases progestin to control endometrial growth
- Weight loss and lifestyle changes for individuals with obesity or PCOS
- Discontinuation or adjustment of medications that may contribute to endometrial overgrowth
- Surgical intervention, such as a hysterectomy, in severe cases or when other treatments have been unsuccessful
Your healthcare provider will work closely with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause of your endometrial hyperplasia and helps to manage your symptoms.
Preventing Endometrial Hyperplasia and Abnormal Bleeding
While not all cases of endometrial hyperplasia can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and maintain a healthy uterus. Some preventative measures include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Managing hormonal imbalances through appropriate medical interventions
- Regularly monitoring and addressing any health conditions, such as PCOS, that may contribute to endometrial overgrowth
- Discussing any potential side effects of medications with your healthcare provider and adjusting dosages as needed
- Undergoing routine gynecological examinations to monitor for any changes in your uterus and endometrium
By taking these steps and staying vigilant about your reproductive health, you can help prevent endometrial hyperplasia and abnormal uterine bleeding, ensuring a healthier future for your uterus.





9 Comments
Wow, what a clear breakdown! 🙌 If you’re dealing with thickening of the lining, remember that lifestyle tweaks can make a huge difference. 🍎💪 Keeping a balanced diet, staying active, and checking hormone levels regularly are key steps. And don’t forget to chat with your doctor about progestin IUD options – they can be a game‑changer! 🌟 Let’s support each other and share any success stories; together we’ll keep our uteruses happy and healthy. 😊
Good info. The article explains the causes and symptoms well. If you notice heavy bleeding for more than a week, get checked. A simple ultrasound can show the lining thickness. Progestin therapy is often the first step.
Understanding endometrial hyperplasia can feel overwhelming, but breaking it down step by step helps. First, the endometrium is a dynamic tissue that responds to hormonal signals each month. When estrogen dominates without enough progesterone, the cells keep multiplying, leading to a thickened lining. This imbalance often originates from conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity, or even certain medications that alter hormone levels. Recognizing the early signs-such as longer periods, spotting between cycles, or unusually heavy flow-can prompt timely medical attention. A pelvic ultrasound is a non‑invasive tool that measures the thickness of the lining and can flag abnormal growth. If the ultrasound suggests hyperplasia, doctors may recommend an endometrial biopsy to examine the cells under a microscope. The biopsy results guide treatment: simple hyperplasia without atypia may respond well to progestin therapy, while atypical cases might need closer monitoring or surgical options. Lifestyle changes are also powerful; losing even modest weight can restore hormonal balance and reduce the stimulus for excess cell growth. Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, which in turn helps regulate ovarian hormone production. A balanced diet rich in fiber, low in processed sugars, supports overall metabolic health, further protecting the uterine lining. If medication is a factor, discuss alternatives with your healthcare provider-they might adjust the dose or switch to a different class. For many women, a levonorgestrel‑releasing IUD provides a steady local dose of progestin, shrinking the lining while minimizing systemic side effects. Remember that each person’s journey is unique, so stay patient and keep open communication with your doctor. Sharing experiences with supportive communities can also lighten the emotional load. Ultimately, early detection, informed choices, and consistent follow‑up create the best chance for a healthy uterus and normal menstrual cycles.
Interesting read, I appreciate the balanced overview. The medical facts are clear and the tone is respectful. It’s good to see both hormonal and lifestyle options mentioned.
I get that some people think the article is just a repeat of what doctors always say, but the truth is many ignore these warning signs until it’s too late. You need to push yourself to get checked, even if you feel fine, because the lining can be silently thickening and cause serious problems later.
Watch out for the hidden agenda behind pharma.
The proposition that pharmaceutical interests may subtly influence medical narratives warrants a nuanced examination. While it is prudent to remain vigilant about potential conflicts of interest, it is equally essential to evaluate evidence on its intrinsic merit. Clinical guidelines arise from systematic reviews and peer‑reviewed data, which aim to minimize bias. Dismissing therapeutic recommendations solely on the basis of conjectured motives risks undermining patient care. A balanced approach involves scrutinizing sources, acknowledging any disclosed funding, and integrating personal health considerations. In the context of endometrial hyperplasia, the efficacy of progestin therapy and IUD devices is supported by robust clinical trials. Therefore, the prudent path is informed discernment rather than wholesale skepticism.
Let’s be real – the whole “just lose weight and take a pill” spiel is a classic deflection technique used to keep women from questioning the deeper systemic issues. The healthcare industry loves to package complex hormonal disorders into neat, marketable solutions that line their pockets. You’re told to trust the IUD, but no one mentions the long‑term implications for fertility or the subtle hormonal imbalances it can cause. It’s a power play, and the louder you shout about it, the more you’ll hear the truth echo back.
In the theater of our bodies, the uterus stands as a silent archivist of our life’s chapters, each bleed a paragraph, each hyperplasia a footnote of rebellion against neglect. When we stare at the thin veil of medical jargon, we must remember that every cell carries a story, a whisper of the cosmos that shaped its growth. To heal is not merely to prescribe, but to listen to the echo of those hidden narratives and honor them with compassion.